Have you ever felt like your body is running on overdrive, maybe a bit too fast for comfort? You know, like things are just moving quicker than they should? For many people, this feeling could point to something called hyperthyroidism, which is a condition where your thyroid gland, a small but very important part of your body, starts making more hormones than is really needed. It's something that can truly affect how you feel day to day, and it's certainly worth taking a closer look at, you know, just to get a better sense of what's happening.
This condition, often called an overactive thyroid, happens when that small gland in your neck releases too much thyroid hormone. So, in a way, it's almost like your body's internal speed dial gets turned up a bit too high. These hormones, you see, play a really big part in how your body uses energy, and when there's an excess, it can lead to a whole bunch of changes you might notice. It’s a common health concern, and many folks are looking for clear, helpful information about it, as of .
Learning about hyperthyroidism means getting to grips with its causes, what signs to look out for, how doctors figure out if you have it, and what choices are available for getting things back to a more balanced state. We're here to help you get a clearer picture of this condition, so you can feel more informed and, perhaps, a bit more at ease. It’s important to understand what your body might be trying to tell you, really.
Table of Contents
- What is Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)?
- Common Signs and Symptoms
- What Brings It On? Causes of Hyperthyroidism
- Getting a Diagnosis: How Doctors Figure It Out
- Pathways to Feeling Better: Treatment Options
- Frequently Asked Questions About Hyperthyroidism
What is Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)?
Hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, is a condition where your thyroid gland makes and then lets out high levels of thyroid hormone. This gland, which is shaped a bit like a butterfly, sits right at the front of your neck, and it's pretty important, actually. It's the part of your body that produces these hormones, which are essential for many different body functions. When this gland is overactive, it means it's producing more of a specific hormone, called thyroxine, than your body truly needs, you know, for its regular operations.
This condition, when the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone, is also called an overactive thyroid. So, if you hear someone say "overactive thyroid," they are talking about hyperthyroidism, basically. It's a way of saying that your thyroid is working a bit too hard, perhaps producing more of these crucial hormones than is healthy for your system. This extra hormone really gets things moving inside your body, and that can show up in a lot of different ways.
The condition is an endocrine disease, which is a way of saying it has to do with your body's hormone system. It's when the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. So, what happens is that these elevated levels of thyroid hormones can lead to a state called thyrotoxicosis. This term, thyrotoxicosis, is used to describe the set of physical and mental changes that happen because there's just too much thyroid hormone circulating in your system, you know, making things speed up.
Common Signs and Symptoms
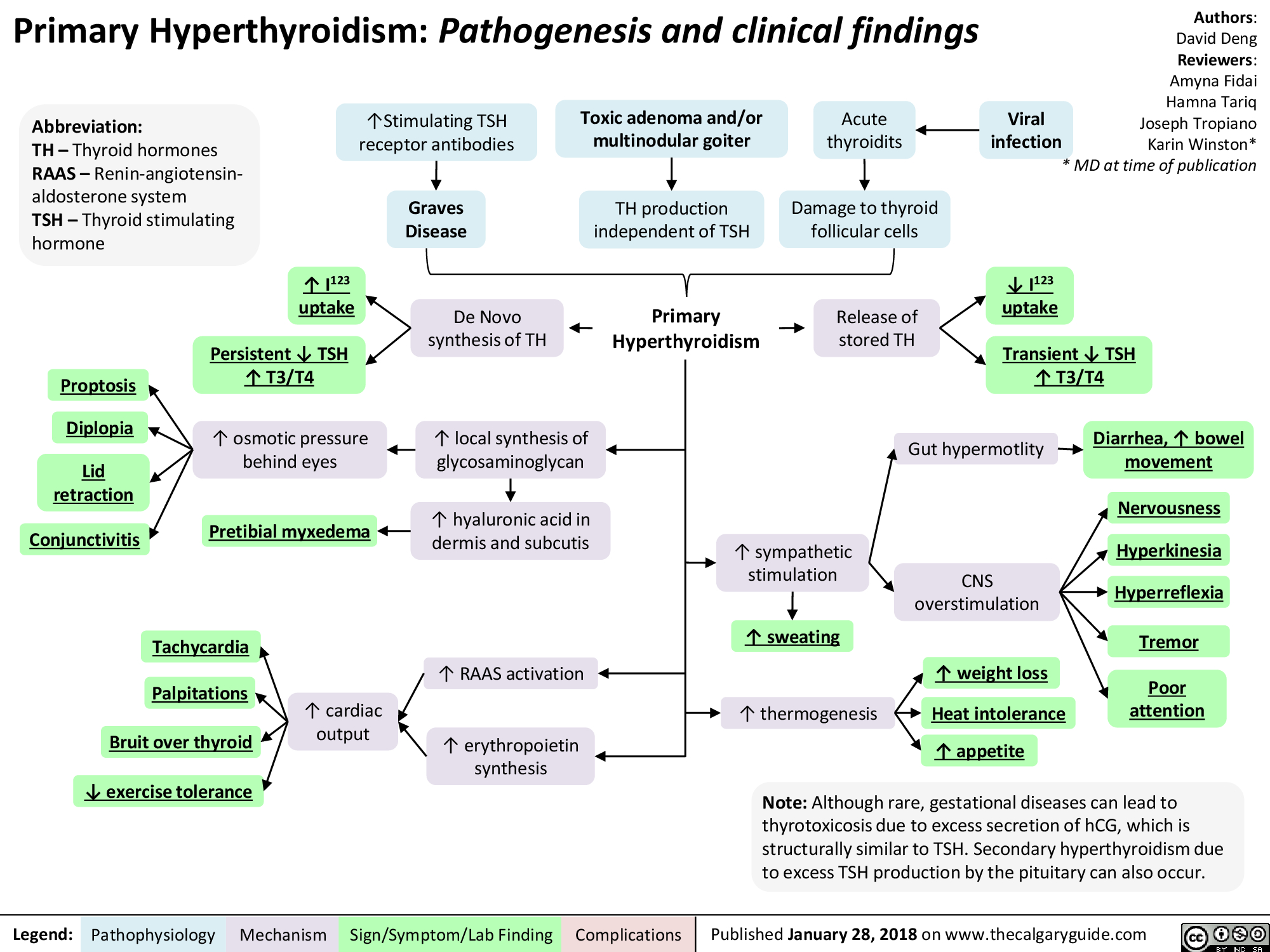
When your thyroid is putting out too much hormone, it really speeds up several bodily functions. This can cause a whole range of symptoms that people might notice. For example, some people find they are losing weight without even trying, which can be a bit surprising. This happens even if they are eating the same amount, or even more, food than they usually do, you know, because their metabolism is running so fast.
Another common sign is having a rapid heart rate, or feeling like your heart is pounding or fluttering. You might also notice you're feeling a bit shaky, especially in your hands. This tremor can be quite noticeable for some. People with an overactive thyroid often feel unusually warm or sweat more than usual, even when others around them are comfortable, so it's almost like their internal thermostat is set too high.
Beyond these, hyperthyroidism can cause difficulty breathing for some people, or a feeling of being short of breath, which is quite concerning. Fatigue, a persistent feeling of tiredness or lack of energy, is also a very common complaint, which seems a bit counterintuitive since the body is speeding up, but it really drains your energy stores. Diarrhea can also be a symptom, as the digestive system also speeds up. You might also experience changes in your sleep patterns, finding it harder to fall asleep or stay asleep.
Some people might also notice changes in their eyes, like a staring gaze, or even bulging eyes in some cases, particularly with a specific cause of hyperthyroidism. There can be changes in your skin and hair, too, perhaps feeling more brittle or oily. You know, it's pretty clear that when your thyroid releases more hormones than you need, it increases your metabolism and affects your body in many different ways, so it's worth paying attention to these signals.
What Brings It On? Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism typically comes about because of a few different reasons, actually. The most common cause, by far, is an autoimmune condition called Graves' disease. In this situation, your body's immune system, which is supposed to protect you from germs, mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. This attack, in a way, makes the thyroid gland produce too much thyroid hormone, rather than slowing it down, which is quite unusual for an autoimmune response.
Another way hyperthyroidism can develop is from thyroid nodules, which are lumps or growths within the thyroid gland. Sometimes, these nodules can become "hot" nodules, meaning they start producing thyroid hormone on their own, outside of the normal control mechanisms. So, you might have one or more of these nodules, and they just start pumping out extra hormone, leading to an overactive state.
Then there's thyroiditis, which is when the thyroid gland becomes inflamed. This inflammation can cause the stored thyroid hormone to leak out of the gland, leading to a temporary increase in hormone levels. This can happen after a pregnancy, or sometimes after a viral infection. It’s a bit different because it's often a temporary situation, unlike Graves' disease or hot nodules, which tend to be more ongoing conditions, you know.
Sometimes, taking too much thyroid hormone medication, if you are being treated for an underactive thyroid, can also lead to hyperthyroidism. This is why it's so important to have your medication dosage carefully monitored by a healthcare provider. So, really, there are a few distinct paths that can lead to your thyroid making more hormones than your body truly needs, and each one needs a slightly different approach to understand and manage.
Getting a Diagnosis: How Doctors Figure It Out
If you or your doctor suspect you might have hyperthyroidism, getting a proper diagnosis is the very next step. The process usually starts with your doctor asking you about your symptoms and doing a physical examination. They'll probably check your neck for any swelling in the thyroid gland and listen to your heart to check for a rapid or irregular beat, you know, just to get a basic idea.
The main way to confirm hyperthyroidism is through blood tests. These tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones in your blood, especially thyroxine, which is a key hormone produced by the thyroid. They also measure thyroid-stimulating hormone, or TSH, which is made by a different gland in your brain and tells your thyroid how much hormone to make. With hyperthyroidism, your thyroxine levels will typically be high, and your TSH levels will usually be quite low, because your body is trying to tell the thyroid to slow down, but it's not listening, in a way.
Sometimes, additional tests might be needed to figure out the exact cause of the hyperthyroidism. For example, a radioactive iodine uptake test might be done. This test helps doctors see how much iodine your thyroid gland is taking up, which can indicate if it's overactive. An ultrasound of the thyroid gland can also be helpful to look for nodules or inflammation, you know, to get a visual of the gland itself. These tests help your doctor paint a complete picture and decide on the best way forward for you.
Pathways to Feeling Better: Treatment Options
Once hyperthyroidism is diagnosed, there are several ways to treat it, with the goal of bringing your thyroid hormone levels back to a normal, healthy range. The choice of treatment often depends on what's causing your hyperthyroidism, how severe your symptoms are, and your overall health, so it's a very personalized decision, really.
One common approach involves using anti-thyroid medications. These medicines work by reducing the amount of hormone your thyroid gland produces. They don't cure the underlying problem, but they do help to control the symptoms by bringing hormone levels down. You usually take these pills for a period of time, and your doctor will monitor your blood levels regularly to adjust the dose as needed, you know, to find that right balance.
Another treatment option is radioactive iodine therapy. This involves taking a small dose of radioactive iodine, usually as a pill. The thyroid gland naturally absorbs iodine, so the radioactive iodine goes directly to the overactive thyroid cells and destroys them, which reduces the amount of hormone the gland makes. This is a pretty effective treatment for many people, and it tends to be a permanent solution for the overactive gland, so it’s something to consider.
For some people, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland might be the best option. This is called a thyroidectomy. It's usually considered when other treatments haven't worked, or if there's a large goiter (an enlarged thyroid gland) that's causing problems with breathing or swallowing. After surgery, people often need to take thyroid hormone replacement pills for the rest of their lives, because their body won't be making enough hormone on its own, you know, to keep things balanced.
Sometimes, beta-blockers are used to help manage the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, especially a rapid heart rate, nervousness, and tremors. These medications don't affect the thyroid hormone levels themselves, but they can make you feel a lot more comfortable while other treatments are working to bring your hormone levels down. It’s important to talk openly with your healthcare provider about all the choices, so you can pick the path that feels right for you and your situation, you know, to get back to feeling like yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hyperthyroidism
What happens if you have hyperthyroidism?
If you have hyperthyroidism, it means your thyroid gland is overactive and produces too much of a hormone called thyroxine. This speeds up several bodily functions, causing symptoms like weight loss even when you're eating, a rapid heart rate, feeling shaky, sweating a lot, and sometimes even diarrhea or feeling very tired. It truly affects your body in many different ways, you know, making things run faster than they should.
What are the warning signs of hyperthyroidism?
Some warning signs to look out for include unexplained weight loss, feeling your heart beat very fast or irregularly, trembling hands, increased sweating, feeling unusually warm, and often feeling quite tired despite your body speeding up. You might also notice changes in your mood, like feeling more anxious or irritable. It’s important to pay attention to these changes, as they can be your body trying to tell you something, really.
What foods to avoid if you have hyperthyroidism?
While there isn't a strict "avoid" list that cures hyperthyroidism, some people with an overactive thyroid might find it helpful to limit foods high in iodine, as iodine is what the thyroid uses to make hormones. This could include things like seaweed, kelp, or some seafood. It’s always best to talk with your doctor or a dietitian about your diet, as they can give you personalized advice based on your specific condition, you know, to make sure you're getting what your body needs.
For more detailed information about your thyroid health, you can Learn more about thyroid conditions on our site, and also check out general health information from a trusted health organization like the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. You can also find more information on this specific page here.
Hyperthyroidism is a condition that can certainly impact your daily life, but with the right information and care, it's something that can be managed effectively. Understanding what's happening in your body is the first step toward feeling better and getting back to a more balanced state. If you suspect you might have hyperthyroidism, reaching out to a healthcare professional is always the best course of action. They can help you figure out what's going on and what steps to take next, you know, to get you on the path to feeling well again.

Detail Author:
- Name : Loyal Sawayn MD
- Username : vwolff
- Email : ldouglas@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1983-01-10
- Address : 847 Hyatt Walk Liamouth, KS 51694
- Phone : +1 (682) 956-1800
- Company : Lind, Towne and Zboncak
- Job : Roofer
- Bio : Vel fuga vel culpa necessitatibus ut est animi. Adipisci saepe at perspiciatis ratione. Cumque quo adipisci praesentium aliquam.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/johanna3658
- username : johanna3658
- bio : Exercitationem ullam rem vel nostrum enim.
- followers : 833
- following : 2009
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/jnienow
- username : jnienow
- bio : Qui consectetur unde veritatis eum est consequatur deleniti.
- followers : 6318
- following : 1456
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/johanna_official
- username : johanna_official
- bio : Ad ipsa ratione nihil sed sed iusto maiores. Maxime quisquam eum modi et distinctio inventore.
- followers : 3918
- following : 1215